The BioASQ challenge comprises the following tasks.
Running tasks
BioASQ Task b on Biomedical Semantic QA (involves IR, QA, summarization and more)
This task uses benchmark datasets containing development and test questions, in English, along with gold standard (reference) answers constructed by a team of biomedical experts. The participants have to respond with relevant concepts, articles, snippets and RDF triples, from designated resources, as well as exact and 'ideal' answers.
BioASQ Task Synergy on Biomedical Semantic QA for developing issues
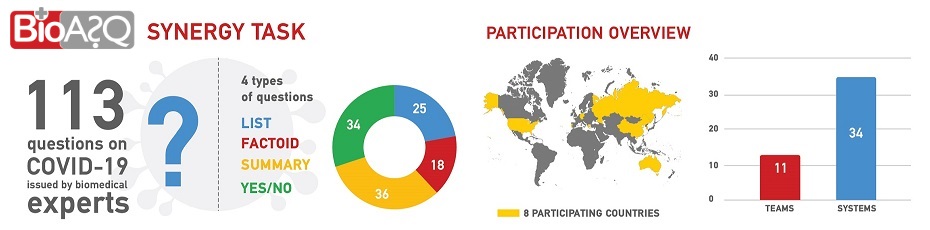
In this task, biomedical experts pose unanswered questions for developing biomedical and public health issues, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Participating systems are required to provide answers, which will in turn be assessed by the experts and fed back to the systems, together with updated questions. This task involves IR, QA, summarization and more on an continuously expanding dataset of documents. Through this process, this task aims to facilitate the incremental understanding of developing health issues, such as COVID-19, and contribute to the discovery of new solutions.
BioASQ Task MultiCardioNER on Multiple clinical entity detection in multilingual medical content
Task MultiCardioNER focuses on the multilingual adaptation of clinical NER systems to the cardiology domain. It uses a combination of two existing datasets (DisTEMIST for diseases and the newly-released DrugTEMIST for medications), as well as a new dataset of cardiology clinical cases annotated using the same guidelines that is used for validation and testing. Participants are asked to create disease-entity recognition systems in Spanish (Track 1), as well as medication-entity recognition systems in three languages: Spanish, English and Italian (Track 2).
The BioASQ Task MultiCardioNER is co-ogranized with the Barcelona Supercomputing Center.
BioASQ Task BioNNE on Nested NER in Russian and English
This task focuses on on nested named entity recognition (NER) in PubMed abstracts in Russian and English. The train/dev datasets include annotated mentions of disorders, anatomical structures, chemicals, diagnostic procedures, and biological functions. Participants are encouraged to apply cross-language (Russian to English) and cross-domain techniques.
The BioASQ Task BioNNE is co-ogranized with the Kazan Federal University.
Completed tasks
BioASQ Task a on Large-Scale Online Biomedical Semantic Indexing
In this task, the participants are asked to classify new PubMed documents, before PubMed curators annotate (in effect, classify) them manually. The classes come from the MeSH hierarchy. As new manual annotations become available, they are used to evaluate the classification performance of participating systems.
In 2022 BioASQ Task a copmleted ten years of pushing the research in biomedical semantic indexing forward. During these ten years, the methods developed by participants for indexing the biomedical literature achieved significant improvements of about 10%. The high point for this task was the recent adoption of fully automated indexing by NLM in mid-2022. Therefore, ten years after its initial introduction, this task fulfilled its goal of facilitating the advancement of biomedical semantic indexing research.
BioASQ Task MedProcNER on MEDical PROCedure Named Entity Recognition
This task focuses on the detection, normalization and indexing of clinical procedures in medical documents in Spanish. Participating systems are challenged to create systems for three subtasks: (a) clinical procedure detection, (b) entity normalization to SNOMED CT and (c) whole document indexing using SNOMED CT codes.
The BioASQ Task MedPRocNER was co-ogranized with the Barcelona Supercomputing Center in 2023. Read more...
BioASQ Task DisTEMIST on Disease Text Mining and Indexing
This task focuses on the recognition and indexing of diseases in medical documents, by posing subtasks of indexing medical documents with controlled terminologies on (1) automatic detection of textual evidence, i.e. disease entity mentions in text (DisTEMIST-Entities), and (2) normalization of these disease mentions to terminologies (DisTEMIST-Linking).
The BioASQ Task DisTEMIST was co-ogranized with the Barcelona Supercomputing Center in 2022. Read more...
BioASQ Task MESINESP on Medical Semantic Indexing In Spanish
This task addresses the automatic indexing with structured medical vocabularies (DeCS terms) of documents from scientific literature (MESINESP-L), clinical trials (MESINESP-T) and patents (MESINESP-P) written in Spanish. The main aim is to promote the development of semantic indexing tools of practical relevance of non-English content, determining the current-state-of-the art, identifying challenges and comparing the strategies and results to those published for English data.
This task was introduced in 2020 with a single batch on indexing scientific literature from the IBECS and LILACS databases. In 2021, the task was extented to the indexing of clinical trials and patents as well. The BioASQ Task MESINESP was co-ogranized with the Barcelona Supercomputing Center. Read more...
BioASQ Task c on Funding Information Extraction From Biomedical Literature
In this task, the participants are asked to extract grant ids and grant agencies from the full text of PumMed documents, available in PubMed Central. Annotations from PubMed are used to evaluate the information extraction performance of participating systems. This task took place as a single test batch in 2017.
Read more